Predictions
The Predictions category provides a solution for using AI and ML cloud services to enhance your application. Some supported use cases:
- Translating text from one language to another
- Converting text to speech
- Text recognition from image
- Entities recognition
- Label real world objects
- Interpretation of text
- Uploading images for automatic training
- Transcribing text
Predictions comes with built-in support for Amazon Translate, Amazon Polly, Amazon Transcribe, Amazon Rekognition, Amazon Textract, and Amazon Comprehend.
Additionally Predictions supports generic invocation of SageMaker Inference API from a native (iOS/Android) application.
Prerequisite: Install and configure the Amplify CLI
Recommendation: Complete the Getting Started guide
Automated Setup
Run the following command in your project’s root folder:
$ amplify init
$ amplify add predictions
The CLI will prompt configuration options for the Predictions category such as what type of use case you have (identifying objects from an image, translating text, etc) and default or advanced settings.
The Predictions category utilizes the Auth category behind the scenes to authorize your app to perform AI/ML actions.
The add command automatically creates the backend configuration. Once all your configuration is complete run the following:
$ amplify push
A configuration file called aws-exports.js will be copied to your configured source directory, for example ./src.
Configure Your App
Import and load the configuration file in your app. It’s recommended you add the Amplify configuration step to your app’s root entry point. For example App.js in React or main.ts in Angular or Ionic.
import Amplify from '@aws-amplify/core';
import Predictions, { AmazonAIPredictionsProvider } from '@aws-amplify/predictions';
import awsconfig from './aws-exports';
Amplify.configure(awsconfig);
Amplify.addPluggable(new AmazonAIPredictionsProvider());
Manual Setup
The manual setup enables you to use your existing Amazon AI and ML resources in your app.
import Amplify from 'aws-amplify';
Amplify.configure({
// To get the AWS Credentials, you need to configure
// the Auth module with your Cognito Federated Identity Pool
"Auth": {
"identityPoolId": "us-east-1:xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx",
"region": "us-east-1"
},
"predictions": {
"convert": {
"translateText": {
"region": "us-east-1",
"proxy": false,
"defaults": {
"sourceLanguage": "en",
"targetLanguage": "zh"
}
},
"speechGenerator": {
"region": "us-east-1",
"proxy": false,
"defaults": {
"VoiceId": "Ivy",
"LanguageCode": "en-US"
}
},
"transcription": {
"region": "us-east-1",
"proxy": false,
"defaults": {
"language": "en-US"
}
}
},
"identify": {
"identifyText": {
"proxy": false,
"region": "us-east-1",
"defaults": {
"format": "PLAIN"
}
},
"identifyEntities": {
"proxy": false,
"region": "us-east-1",
"celebrityDetectionEnabled": true,
"defaults": {
"collectionId": "identifyEntities8b89c648-test",
"maxEntities": 50
}
},
"identifyLabels": {
"proxy": false,
"region": "us-east-1",
"defaults": {
"type": "LABELS"
}
}
},
"interpret": {
"interpretText": {
"region": "us-east-1",
"proxy": false,
"defaults": {
"type": "ALL"
}
}
}
}
});
IAM Policy
The Amplify CLI will set appropriate IAM policy for Roles in your Cognito Identity Pool in order to use an appropriate feature. If you are using the library manually you will need to configure this yourself. The below policy demonstrates setting policy for all services in the Predictions category:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"translate:TranslateText",
"polly:SynthesizeSpeech",
"transcribe:StartStreamTranscriptionWebSocket",
"comprehend:DetectSentiment",
"comprehend:DetectEntities",
"comprehend:DetectDominantLanguage",
"comprehend:DetectSyntax",
"comprehend:DetectKeyPhrases",
"rekognition:DetectFaces",
"rekognition:RecognizeCelebrities"
"rekognition:DetectLabels",
"rekognition:DetectModerationLabels",
"rekognition:DetectText",
"rekognition:DetectLabel",
"textract:AnalyzeDocument",
"textract:DetectDocumentText",
"textract:GetDocumentAnalysis",
"textract:StartDocumentAnalysis",
"textract:StartDocumentTextDetection",
"rekognition:SearchFacesByImage"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
]
}
For rekognition:SearchFacesByImage you can scope the Resource down to an individual collection such as arn:aws:rekognition:<REGION>:<ACCOUNT_ID>:collection/<COLLECTION_ID>. Amplify CLI automatically does this.
Use cases
Predictions is broadly organized into 3 key use cases - Identify, Convert, and Interpret - which are available in the client API as well as CLI workflows.
Identify will find text (words, tables, pages from a book), entities (faces and/or celebrities) from images. You can also identify real world objects such as chairs, desks, etc. which are referred to as “labels” from images. Convert allows you to translate text from one source language to a target language. You can also generate speech audio from text input. Lastly, you can take an audio input and transcribe it using a websocket stream. Finally Interpret allows you to analyze text for language, entities (places, people), key phrases, sentiment (positive, neutral, negative), and syntax (pronouns, verbs, adjectives).
Some common use cases are listed below, as well as an advanced workflow which allows you to perform dynamic image indexing from your client application.
Translate Text
If you haven’t already done so, run amplify init inside your project and then amplify add auth (we recommend selecting the default configuration).
Run amplify add predictions and select Convert. Then use the following answers:
? What would you like to convert? (Use arrow keys)
❯ Convert text into a different language
Convert text to speech
Convert speech to text
Learn More
? Who should have access? Auth and Guest users
Now run amplify push which will generate your aws-exports.js and create resources in the cloud. You can now either add this to your backend or skip and add more features to your app.
Services used: Amazon Translate
Speech Generation
If you haven’t already done so, run amplify init inside your project and then amplify add auth (we recommend selecting the default configuration).
Run amplify add predictions and select Convert. Then use the following answers:
? What would you like to convert?
Convert text into a different language
❯ Convert text to speech
Convert speech to text
Learn More
? Who should have access? Auth and Guest users
Now run amplify push which will generate your aws-exports.js and create resources in the cloud. You can now either add this to your backend or skip and add more features to your app.
Services used: Amazon Polly
Transcribing audio to text
If you haven’t already done so, run amplify init inside your project and then amplify add auth (we recommend selecting the default configuration).
Run amplify add predictions and select Convert. Then use the following answers:
? What would you like to convert?
Convert text into a different language
Convert text to speech
❯ Convert speech to text
Learn More
? Who should have access? Auth and Guest users
Now run amplify push which will generate your aws-exports.js and create resources in the cloud. You can now either add this to your backend or skip and add more features to your app.
Services used: Amazon Transcribe
Identify Text from a photo
If you haven’t already done so, run amplify init inside your project and then amplify add auth (we recommend selecting the default configuration).
Run amplify add predictions and select Identify. Then use the following answers:
? What would you like to identify? (Use arrow keys)
❯ Identify Text
Identify Entities
Identify Labels
Learn More
? Would you also like to identify documents? Yes
? Who should have access? Auth and Guest users
Now run amplify push which will generate your aws-exports.js and create resources in the cloud. You can now either add this to your backend or skip and add more features to your app.
Services used: Amazon Rekognition (default for plain text) and Amazon Textract (default for documents)
Identify Entities from a photo
Setup your backend with the following:
If you haven’t already done so, run amplify init inside your project and then amplify add auth (we recommend selecting the default configuration).
Run amplify add predictions and select Identify. Then use the following answers:
? What would you like to identify?
Identify Text
❯ Identify Entities
Identify Labels
Learn More
? Would you like use the default configuration? Default Configuration
? Who should have access? Auth and Guest users
Now run amplify push which will generate your aws-exports.js and create resources in the cloud. You can now either add this to your backend or skip and add more features to your app.
Services used: Amazon Rekognition
Advanced configuration
You can enhance your application’s ability to identify entities by performing indexing against a pre-defined collection of images and providing them to Amazon Rekognition. This can be done in one of two ways:
- Administrators provide images to be indexed from an S3 bucket
- Application users upload files to an S3 bucket which are indexed
Amplify configures Lambda Triggers to automatically perform this indexing when the files are uploaded. As Rekognition does not store any faces, but rather the facial features into a vector which are stored in the backend, these images can be deleted after indexing if you choose to do so. However note that by default the Lambda Triggers will remove the index if you delete an image so you will need to modify their behavior if you desire this functionality.
To add this functionality into your application choose advanced when prompted in the Identify flow (if you already enabled Identify Entities you will need to run amplify update predictions):
? What would you like to identify? Identify Entities
? Would you like use the default configuration? Advanced Configuration
? Would you like to enable celebrity detection? Yes
? Would you like to identify entities from a collection of images? Yes
? How many entities would you like to identify 50
? Would you like to allow users to add images to this collection? Yes
? Who should have access? Auth and Guest users
? The CLI would be provisioning an S3 bucket to store these images please provide bucket name: mybucket
Note that if you already have an S3 bucket in your project from running amplify add storage it would be reused. To upload images from the CLI for administrator indexing, you can run amplify predictions console and select Identify which will open the S3 bucket location in the AWS console for you to upload your images.
For application users, when they upload images with Storage.put() they will specify a prefix which the Lambda functions perform indexing like so:
Storage.put('test.jpg', file,
{
level: 'protected',
customPrefix: {
protected: 'protected/predictions/index-faces/',
}
});
In the sample React application code below, you will see that to use this functionality you will need to set collection:true when calling Predictions.identify() and remove celebrityDetection: true. The flow is that you will first upload an image to S3 with the PredictionsUpload function (which is connected to a button in the app) and after a few seconds you can send this same image to Predictions.identify() and it will check if that image has been indexed in the Collection.
Label Real world objects
If you haven’t already done so, run amplify init inside your project and then amplify add auth (we recommend selecting the default configuration).
Run amplify add predictions and select Identify. Then use the following answers:
? What would you like to identify?
Identify Text
Identify Entities
❯ Identify Labels
Learn More
? Would you like use the default configuration? (Use arrow keys)
❯ Default Configuration
Advanced Configuration
? Who should have access? Auth and Guest users
The Advanced Configuration will allow you to select moderation for unsafe content or all of the identified labels. Default uses both.
Now run amplify push which will generate your aws-exports.js and create resources in the cloud. You can now either add this to your backend or skip and add more features to your app.
Services used: Amazon Rekognition
Text Interpretation
This will allow you to determine key phrases, sentiment analysis from text, etc. If you haven’t already done so, run amplify init inside your project and then amplify add auth (we recommend selecting the default configuration).
Run amplify add predictions and select Interpret. Then use the following answers:
? What would you like to interpret? (Use arrow keys)
❯ Interpret Text
Learn More
? What kind of interpretation would you like?
Language
Entity
Keyphrase
Sentiment
Syntax
❯ All
? Who should have access? Auth and Guest users
Now run amplify push which will generate your aws-exports.js and create resources in the cloud. You can now either add this to your backend or skip and add more features to your app.
Services used: Amazon Comprehend
Sample React app
A sample React application with all of the Predictions features is provided below. It shows how to use all scenarios above by calling the appropriate convert, identify, and interpret API calls in the Amplify library.
To use Predictions.convert() with Amazon Transcribe you will need to install the following dependency in your app first:
yarn add microphone-stream
The components in the app code below are rendered according to the scenarios above like so:
return (
<div className="App">
<TextTranslation />
<br/>
<TextToSpeech />
<br/>
<SpeechToText />
<br/>
<TextIdentification />
<br/>
<EntityIdentification />
<br/>
<PredictionsUpload />
<br/>
<LabelsIdentification />
<br/>
<TextInterpretation />
</div>
);
React app code
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import Amplify, { Storage, Predictions } from 'aws-amplify';
import { AmazonAIPredictionsProvider } from '@aws-amplify/predictions';
import awsconfig from './aws-exports';
import mic from 'microphone-stream';
Amplify.configure(awsconfig);
Amplify.addPluggable(new AmazonAIPredictionsProvider());
function TextIdentification() {
const [response, setResponse] = useState("You can add a photo by uploading direcly from the app ")
function identifyFromFile(event) {
setResponse('identifiying text...');
const { target: { files } } = event;
const [file,] = files || [];
if (!file) {
return;
}
Predictions.identify({
text: {
source: {
file,
},
format: "PLAIN", // Available options "PLAIN", "FORM", "TABLE", "ALL"
}
}).then(({text: { fullText }}) => {
setResponse(fullText)
})
.catch(err => setResponse(JSON.stringify(err, null, 2)))
}
return (
<div className="Text">
<div>
<h3>Text identification</h3>
<input type="file" onChange={identifyFromFile}></input>
<p>{response}</p>
</div>
</div>
);
}
function EntityIdentification() {
const [response, setResponse] = useState("Click upload for test ")
const [src, setSrc] = useState("");
function identifyFromFile(event) {
setResponse('searching...');
const { target: { files } } = event;
const [file,] = files || [];
if (!file) {
return;
}
Predictions.identify({
entities: {
source: {
file,
},
/**For using the Identify Entities advanced features, enable collection:true and comment out celebrityDetection
* Then after you upload a face with PredictionsUpload you'll be able to run this again
* and it will tell you if the photo you're testing is in that Collection or not and display it*/
//collection: true
celebrityDetection: true
}
}).then(result => {
console.log(result);
const entities = result.entities;
let imageId = ""
let names = ""
entities.forEach(({ boundingBox, metadata: { name = "", externalImageId = "" } }) => {
const {
width, // ratio of overall image width
height, // ratio of overall image height
left, // left coordinate as a ratio of overall image width
top // top coordinate as a ratio of overall image heigth
} = boundingBox;
imageId = externalImageId;
if (name) {
names += name + " .";
}
console.log({ name });
})
if (imageId) {
Storage.get("", {
customPrefix: {
public: imageId
},
level: "public",
}).then(setSrc); // this should be better but it works
}
console.log({ entities });
setResponse(names);
})
.catch(err => console.log(err))
}
return (
<div className="Text">
<div>
<h3>Entity identification</h3>
<input type="file" onChange={identifyFromFile}></input>
<p>{response}</p>
{ src && <img src={src}></img>}
</div>
</div>
);
}
function PredictionsUpload() {
/* This is Identify Entities Advanced feature
* This will upload user images to the appropriate bucket prefix
* and a Lambda trigger will automatically perform indexing
*/
function upload(event) {
const { target: { files } } = event;
const [file,] = files || [];
Storage.put(file.name, file, {
level: 'protected',
customPrefix: {
protected: 'protected/predictions/index-faces/',
}
});
}
return (
<div className="Text">
<div>
<h3>Upload to predictions s3</h3>
<input type="file" onChange={upload}></input>
</div>
</div>
);
}
function LabelsIdentification() {
const [response, setResponse] = useState("Click upload for test ")
function identifyFromFile(event) {
const { target: { files } } = event;
const [file,] = files || [];
if (!file) {
return;
}
Predictions.identify({
labels: {
source: {
file,
},
type: "ALL" // "LABELS" will detect objects , "UNSAFE" will detect if content is not safe, "ALL" will do both default on aws-exports.js
}
}).then(result => setResponse(JSON.stringify(result, null, 2)))
.catch(err => setResponse(JSON.stringify(err, null, 2)))
}
return (
<div className="Text">
<div>
<h3>Labels identification</h3>
<input type="file" onChange={identifyFromFile}></input>
<p>{response}</p>
</div>
</div>
);
}
function SpeechToText(props) {
const [response, setResponse] = useState("Press 'start recording' to begin your transcription. Press STOP recording once you finish speaking.")
function AudioRecorder(props) {
const [recording, setRecording] = useState(false);
const [micStream, setMicStream] = useState();
const [audioBuffer] = useState(
(function() {
let buffer = [];
function add(raw) {
buffer = buffer.concat(...raw);
return buffer;
}
function newBuffer() {
console.log("reseting buffer");
buffer = [];
}
return {
reset: function() {
newBuffer();
},
addData: function(raw) {
return add(raw);
},
getData: function() {
return buffer;
}
};
})()
);
async function startRecording() {
console.log('start recording');
audioBuffer.reset();
window.navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia({ video: false, audio: true }).then((stream) => {
const startMic = new mic();
startMic.setStream(stream);
startMic.on('data', (chunk) => {
var raw = mic.toRaw(chunk);
if (raw == null) {
return;
}
audioBuffer.addData(raw);
});
setRecording(true);
setMicStream(startMic);
});
}
async function stopRecording() {
console.log('stop recording');
const { finishRecording } = props;
micStream.stop();
setMicStream(null);
setRecording(false);
const resultBuffer = audioBuffer.getData();
if (typeof finishRecording === "function") {
finishRecording(resultBuffer);
}
}
return (
<div className="audioRecorder">
<div>
{recording && <button onClick={stopRecording}>Stop recording</button>}
{!recording && <button onClick={startRecording}>Start recording</button>}
</div>
</div>
);
}
function convertFromBuffer(bytes) {
setResponse('Converting text...');
Predictions.convert({
transcription: {
source: {
bytes
},
// language: "en-US", // other options are "en-GB", "fr-FR", "fr-CA", "es-US"
},
}).then(({ transcription: { fullText } }) => setResponse(fullText))
.catch(err => setResponse(JSON.stringify(err, null, 2)))
}
return (
<div className="Text">
<div>
<h3>Speech to text</h3>
<AudioRecorder finishRecording={convertFromBuffer} />
<p>{response}</p>
</div>
</div>
);
}
function TextToSpeech() {
const [response, setResponse] = useState("...")
const [textToGenerateSpeech, setTextToGenerateSpeech] = useState("write to speech");
function generateTextToSpeech() {
setResponse('Generating audio...');
Predictions.convert({
textToSpeech: {
source: {
text: textToGenerateSpeech,
},
voiceId: "Amy" // default configured on aws-exports.js
// list of different options are here https://docs.aws.amazon.com/polly/latest/dg/voicelist.html
}
}).then(result => {
let AudioContext = window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext;
console.log({ AudioContext });
const audioCtx = new AudioContext();
const source = audioCtx.createBufferSource();
audioCtx.decodeAudioData(result.audioStream, (buffer) => {
source.buffer = buffer;
source.connect(audioCtx.destination);
source.start(0);
}, (err) => console.log({err}));
setResponse(`Generation completed, press play`);
})
.catch(err => setResponse(err))
}
function setText(event) {
setTextToGenerateSpeech(event.target.value);
}
return (
<div className="Text">
<div>
<h3>Text To Speech</h3>
<input value={textToGenerateSpeech} onChange={setText}></input>
<button onClick={generateTextToSpeech}>Text to Speech</button>
<h3>{response}</h3>
</div>
</div>
);
}
function TextTranslation() {
const [response, setResponse] = useState("Input some text and click enter to test")
const [textToTranslate, setTextToTranslate] = useState("write to translate");
function translate() {
Predictions.convert({
translateText: {
source: {
text: textToTranslate,
// language : "es" // defaults configured on aws-exports.js
// supported languages https://docs.aws.amazon.com/translate/latest/dg/how-it-works.html#how-it-works-language-codes
},
// targetLanguage: "en"
}
}).then(result => setResponse(JSON.stringify(result, null, 2)))
.catch(err => setResponse(JSON.stringify(err, null, 2)))
}
function setText(event) {
setTextToTranslate(event.target.value);
}
return (
<div className="Text">
<div>
<h3>Text Translation</h3>
<input value={textToTranslate} onChange={setText}></input>
<button onClick={translate}>Translate</button>
<p>{response}</p>
</div>
</div>
);
}
function TextInterpretation() {
const [response, setResponse] = useState("Input some text and click enter to test")
const [textToInterpret, setTextToInterpret] = useState("write some text here to interpret");
function interpretFromPredictions() {
Predictions.interpret({
text: {
source: {
text: textToInterpret,
},
type: "ALL"
}
}).then(result => setResponse(JSON.stringify(result, null, 2)))
.catch(err => setResponse(JSON.stringify(err, null, 2)))
}
function setText(event) {
setTextToInterpret(event.target.value);
}
return (
<div className="Text">
<div>
<h3>Text interpretation</h3>
<input value={textToInterpret} onChange={setText}></input>
<button onClick={interpretFromPredictions}>test</button>
<p>{response}</p>
</div>
</div>
);
}
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
Translate Text
<TextTranslation />
<br/>
Speech Generation
<TextToSpeech />
<br/>
Transcribe Audio
<SpeechToText />
<br/>
Identify Text
<TextIdentification />
<br/>
Identify Entities
<EntityIdentification />
<br/>
Identify Entities (Advanced)
<PredictionsUpload />
<br/>
Label Objects
<LabelsIdentification />
<br/>
Text Interpretation
<TextInterpretation />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Now run yarn start and press the buttons to demo the app.
Sample Ionic app
First, be sure you have the latest Ionic CLI installed, then generate a new app (for this example you can use any template, but it’s simplest to start with the Blank template to start):
$ npm i -g ionic
$ ionic start predictions blank # the first argument is your project name, the second the template
Update the src/polyfills.ts and add to the top of the file (window as any).global = window;. Then, update the src/tsconfig.app.json file and add the “node” types:
{
"extends": "../tsconfig.json",
"compilerOptions": {
"outDir": "../out-tsc/app",
"types": ["node"]
},
"exclude": [
"test.ts",
"**/*.spec.ts"
]
}
src/app/home/home.page.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import Predictions from '@aws-amplify/predictions';
import { TextToSpeechOutput } from '@aws-amplify/predictions/lib/types';
@Component({
selector: 'app-home',
templateUrl: 'home.page.html',
styleUrls: ['home.page.scss'],
})
export class HomePage {
public textToTranslate = "Hello Amplify";
public translateResult = "";
public srcLang = "en";
public targetLang = "de";
public voiceId = "Salli";
public speechUrl:string;
public speakResult:boolean;
constructor() {}
public async translate() {
const result = await Predictions.convert({
translateText: {
source: {
text: this.textToTranslate,
language : this.srcLang
},
targetLanguage: this.targetLang
}
});
this.translateResult = result.text || "Error";
if (this.speakResult) {
this.generateSpeech(result.text);
}
}
public async generateSpeech(textToGenerateSpeech: string) {
const result:TextToSpeechOutput = await Predictions.convert({
textToSpeech: {
source: {
text: textToGenerateSpeech,
},
voiceId: this.voiceId
}
});
const audioCtx = new ((window as any).AudioContext || (window as any).webkitAudioContext)();
const source = audioCtx.createBufferSource();
audioCtx.decodeAudioData(result.audioStream, (buffer) => {
source.buffer = buffer;
source.connect(audioCtx.destination);
source.start(audioCtx.currentTime);
}, (err) => console.log({err}));
}
public selectSource(value: string) {
this.srcLang = value;
}
public selectTarget(value: string) {
this.targetLang = value;
}
}
src/app/home/home.page.html
<ion-header>
<ion-toolbar>
<ion-title>
Amplify Predictions
</ion-title>
</ion-toolbar>
</ion-header>
<ion-content>
<ion-card class="welcome-card">
<ion-card-header>
<ion-card-title>Convert</ion-card-title>
<ion-card-subtitle>Translate languages</ion-card-subtitle>
</ion-card-header>
<ion-card-content>
<ion-list>
<ion-item>
<ion-label>Source Language</ion-label>
<ion-select #srcLang placeholder="Source Language" (ionChange)="selectSource(srcLang.value)">
<ion-select-option value="en" selected>English</ion-select-option>
<ion-select-option value="es">Spanish</ion-select-option>
<ion-select-option value="de">German</ion-select-option>
<ion-select-option value="no">Norwegian</ion-select-option>
</ion-select>
</ion-item>
<ion-item>
<ion-label>Target Language</ion-label>
<ion-select #targetLang placeholder="Target Language" (ionChange)="selectTarget(targetLang.value)">
<ion-select-option value="en">English</ion-select-option>
<ion-select-option value="es">Spanish</ion-select-option>
<ion-select-option value="de" selected>German</ion-select-option>
<ion-select-option value="no">Norwegian</ion-select-option>
</ion-select>
</ion-item>
</ion-list>
<ion-grid>
<ion-row>
<ion-col align-self-center>
<textarea placeholder="Text to translate" [(ngModel)]="textToTranslate" rows="5" cols="30"></textarea>
</ion-col>
</ion-row>
<ion-row>
<ion-col size="6">
<ion-button (click)="translate()" [disabled]="!textToTranslate">Translate</ion-button>
</ion-col>
<ion-col size="6" align-self-center>
<ion-checkbox color="primary" [(ngModel)]="speakResult"></ion-checkbox>
<ion-label>Speak Result</ion-label>
</ion-col>
</ion-row>
<ion-row>
<ion-col align-self-center>
<textarea placeholder="Translation will display here" [value]="translateResult" rows="5" cols="30"></textarea>
</ion-col>
</ion-row>
</ion-grid>
</ion-card-content>
</ion-card>
</ion-content>
Working with the API
Identify text in images
Detect text in an input image. Input can be sent directly from the browser or an Amazon S3 key from project bucket.
Predictions.identify({
text: {
source: file
}
}).then((response) => {...})
From Amazon S3 key
Predictions.identify({
text: {
source: {
key: pathToPhoto,
level?: 'public | private | protected', //optional, default is the configured on Storage category
}
}
}).then((response) => {...})
The following options are independent of which source is specified. For demonstration purposes it will be used file but it can be an S3 Key as well. Predictions.identify({text : {...}}) can detect unstructured text PLAIN, structured text from tables TABLE or text from forms FORM.
For detecting plain text, you can see the whole detected text, the lines detected, the position of each line of text, and each word.
Predictions.identify({
text: {
source: {
file
},
format: "PLAIN",
}
}).then(({
{ text:
{ fullText, // String
lines // Array of String ordered from top to bottom
linesDetailed: {
text, // String
boundingBox: {
width, // ratio of overall image width
height, // ratio of overall image height
left, // left coordinate as a ratio of overall image width
top // top coordinate as a ratio of overall image heigth
},
polygon // Array of { x, y } coordinates as a ratio of overall image width and height
},
words // Array of objects that contains { text, boundingBox, polygon}
}
}) => {...});
For detecting structured forms (documents, tables, etc.) from an image, keyValues will return a string of the entity found in the image as well as metadata such as selected checkboxes or the relative location in the image using a boundingBox.
Predictions.identify({
text: {
source: {
file
},
format: "FORM",
}
}).then(({
{ text:
{
// same as PLAIN +
keyValues
// Array of { key (String), value: { text (String), selected (boolean)}, polygon, boundingBox }
}
}
}) => {...});
For example the below image would return keyValues with “Test” or “Checked” as a key, and true since they are selected. The location of these elements would be returned in the boundingBox value.
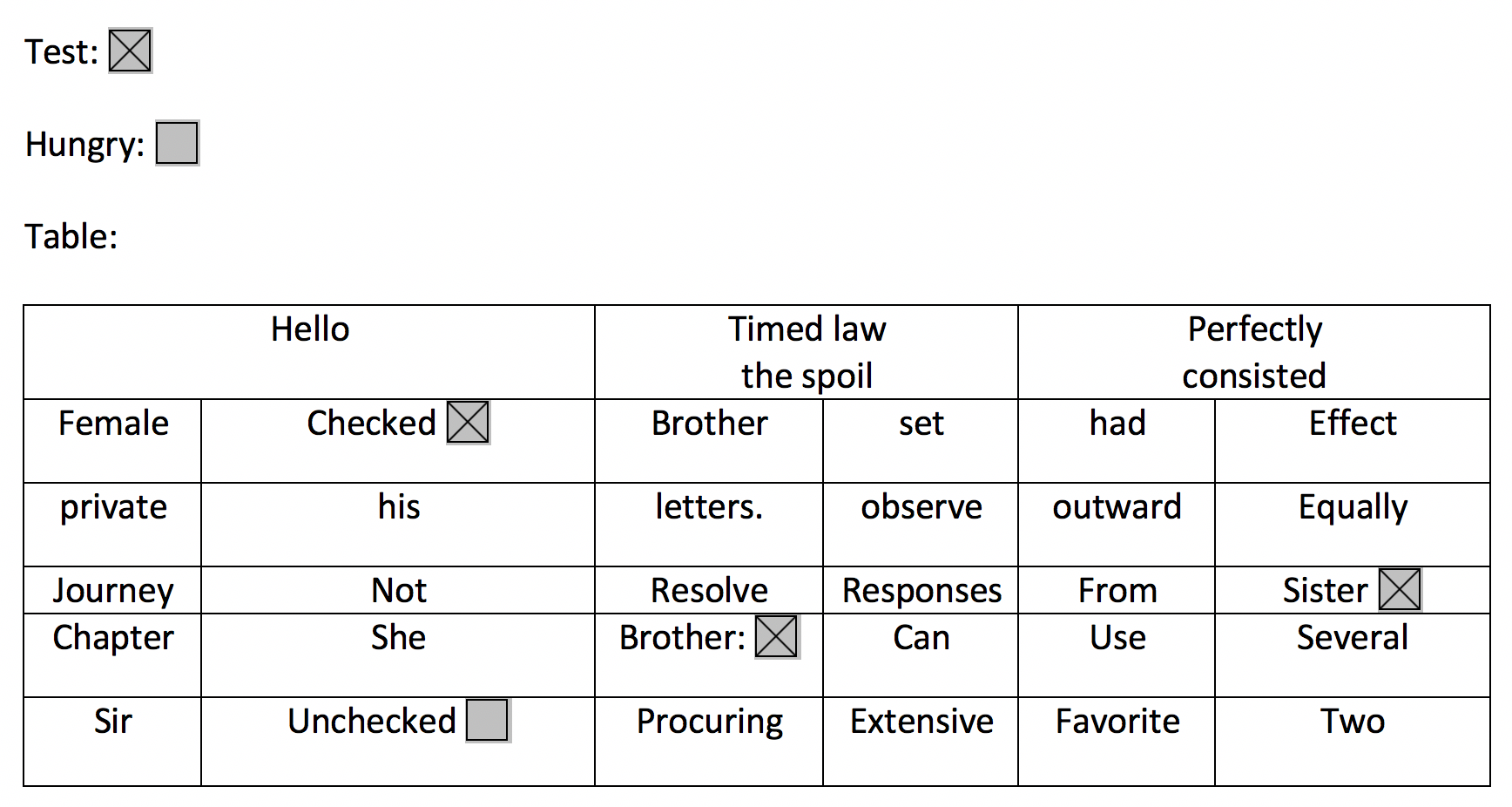
For detecting structured tables from an image
Predictions.identify({
text: {
source: {
file
},
format: "TABLE",
}
}).then(({
{ text:
{
// same as PLAIN +
tables : {
size: { rows, columns },
table // Matrix Array[ Array ] of size rows
// each element of the array contains { text, boundingBox, polygon, selected, rowSpan, columnSpan}
}
}
}
}) => {...});
For detecting tables and forms on the image just select format “ALL”
Predictions.identify({
text: {
source: {
file
},
format: "TABLE",
}
}).then(({
{ text:
{
// same as PLAIN + FORM + TABLE
}
}
}) => {...});
Identify entities in images
Predictions.identify({entities: {...}}) => Promise<>
Detects entities from an image and potentially related information such as position, faces, and landmarks. Can also identify celebrities and entities that were previously added. This function returns a Promise that returns an object with the entities that was identified.
Input can be sent directly from the browser or an Amazon S3 key from project bucket.
Detect entities directly from image uploaded from the browser. (File object)
Predictions.identify({
entities: {
source: {
file,
},
}
}).then((response) => {...})
.catch(err => {...})
}
From Amazon S3 key
Predictions.identify({
entities: {
source: {
key: pathToPhoto,
level?: 'public | private | protected', //optional, default is the configured on Storage category
},
}
}).then((response) => {...})
.catch(err => {...})
The following options are independent of which source is specified. For demonstration purposes it will be used file but it can be used S3 Key as well.
Detecting bounding box of faces from an image with its landmarks (eyes, mouth, nose).
Predictions.identify({
entities: {
source: {
file,
},
}
}).then(({ entities }) => {
entities.forEach(({boundingBox, landmarks}) => {
const {
width, // ratio of overall image width
height, // ratio of overall image height
left, // left coordinate as a ratio of overall image width
top // top coordinate as a ratio of overall image heigth
} = boundingBox;
landmarks.forEach(landmark => {
const {
type, // string "eyeLeft", "eyeRight", "mouthLeft", "mouthRight", "nose"
x, // ratio of overall image width
y // ratio of overall image height
} = landmark;
})
})
.catch(err => {...})
}
Detecting celebrities on an image. It will return only celebrities the name and urls with related information.
Predictions.identify({
entities: {
source: {
file,
},
celebrityDetection: true // boolean. It will only show detected celebreties
}
}).then(({ entities }) => {
entities.forEach(({ boundingBox, landmarks, metadata }) => {
const {
name,
urls
} = metadata; // celebrity info
// ...
})
})
.catch(err => setResponse(JSON.stringify(err, null, 2)))
Detecting entities from previously uploaded images (e.g. Advanced Configuration for Identify Entities)
Predictions.identify({
entities: {
source: {
file,
},
collection: true
}
}).then({entities} => {
entities.forEach(({ boundingBox, metadata: { externalImageId } }) => {
const {
width, // ratio of overall image width
height, // ratio of overall image height
left, // left coordinate as a ratio of overall image width
top // top coordinate as a ratio of overall image heigth
} = boundingBox;
console.log({externalImageId}); // this is the object key on S3 from the original image!
Storage.get("", {
customPrefix: {
public: externalImageId
},
level: "public",
}).then(src => {...}); // this could be improve but
})
})
.catch(err => console.log(err))
}
Identify objects in images
Detects real world objects or unsafe content from an image. This function returns a Promise that returns an object with the objects labeled that was identified.
Labels only
Detect labels, such if an image has a desk or a chair in it
Predictions.identify({
labels: {
source: {
file,
},
type: "LABELS"
}
}).then(response => {
const { labels } = response;
labels.forEach(object => {
const { name, boundingBoxes } = object
});
});
Detect unsafe content in an image
Predictions.identify({
labels: {
source: {
file,
},
type: "UNSAFE"
}
}).then(response => {
const { unsafe } = response; // boolean
});
for both labels and unsafe content
Predictions.identify({
labels: {
source: {
file,
},
type: "ALL"
}
}).then(response => {
const { labels } = response;
const { unsafe } = response; // boolean
labels.forEach(object => {
const { name, boundingBoxes } = object
});
});
Transcribing audio
You can transcribe a PCM Audio byte buffer to Text, such as a recording from microphone.
Predictions.convert({
transcription: {
source: {
bytes
},
// language: "en-US", // other options are "en-GB", "fr-FR", "fr-CA", "es-US"
},
}).then(({ transcription: { fullText } }) => console.log(fullText))
.catch(err => console.log(JSON.stringify(err, null, 2)))
}
Text to Speech
Generate an audio buffer for playback from a text input.
Predictions.convert({
textToSpeech: {
source: {
text: textToGenerateSpeech
},
voiceId: "Amy" // default configured on aws-exports.js
// list of different options are here https://docs.aws.amazon.com/polly/latest/dg/voicelist.html
}
}).then(result => {
})
.catch(err => console.log(JSON.stringify(err, null, 2)))
}
Translation of text
Translate text from one source language to a destination language.
Predictions.convert({
translateText: {
source: {
text: textToTranslate,
// language : "es" // defaults configured on aws-exports.js
// supported languages https://docs.aws.amazon.com/translate/latest/dg/how-it-works.html#how-it-works-language-codes
},
// targetLanguage: "en"
}
}).then(result => console.log(JSON.stringify(result, null, 2)))
.catch(err => console.log(JSON.stringify(err, null, 2)))
Analyze Text
Analyze text to find key phrases, sentiment (positive, negative, neutral), or the syntax (pronouns, verbs, etc.). You can also find entities in the text such as names or places, or perform language detection.
Predictions.interpret({
text: {
source: {
text: textToInterpret,
},
type: "ALL"
}
}).then(result => console.log(JSON.stringify(result, null, 2)))
.catch(err => console.log(JSON.stringify(err, null, 2)))



